import clr (1)
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.TypeAndResult') (2)
from Loehnert.TypeAndResult import Station (3)
station = Station('my_station') (4)Python examples
5 minute read
Creating an instance of a .NET class
This example shows how to add a .NET-Assembly as a reference to the CLR (Common Language Runtime) and how to create an instance of a class.
| 1 | Import of the CLR (Common Language Runtime) module |
| 2 | To use a .NET assembly, it must be added to the CLR as a reference |
| 3 | Import the Station type from the Loehnert.TypeAndResult namespace |
| 4 | Calling the constructor |
| Find many useful tips on .NET integration in the IronPython .NET integration documentation. |
| The assemblies system and mscorlib do not have to be added as a clr reference, because they are automatically loaded from the DLR (Dynamic Language Runtime) by default. |
Creating a measure cycle and evaluating an attribute
Create a measure cycle and a measure process and evaluate an attribute. The station has a TypeData module and a WorkPiece module. The type data from the type data example are loaded.
WorkPiece.SetWorkPiece('1234') (1)
measure_cycle = WorkPiece.GetNewMeasureCycle() (2)
measure_process = measure_cycle.AddNewMeasureProcess('HighVoltageTest') (3)
current = 0.004 # 4mA (4)
measure_process.EvaluateAttribute('Current', current) (5)
measure_process.Evaluate() (6)
measure_cycle.Evaluate() (7)
WorkPiece.RemoveWorkPiece() (8)| 1 | Load the workpiece (test item) via an ID. The unique ID 1234 could be a trace ID or a serial number |
| 2 | Create a measuring cycle for a workpiece |
| 3 | Create a measuring process for the HighVoltageTest process |
| 4 | Generate measured value, this would be generated by a measuring device |
| 5 | Evaluate Current attribute |
| 6 | Evaluate measure process |
| 7 | Evaluate measuring cycle |
| 8 | Remove workpiece from the workpiece module |
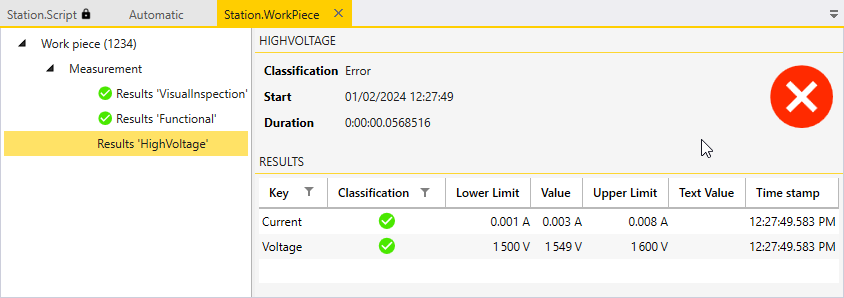
Figure 1 shows the result view in the service window of the WorkPiece module. The overall classification of the measure cycle is rated as "Fail" in the selected example because not all attributes of the HighVoltage process were measured.
Display a dialog
This example shows you how to display a dialogue with an input field.
import clr
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.Controls') (1)
from Loehnert.Controls.Dialogs import DialogService
dialog = DialogService.GetDialogBuilder()\ (2)
.WithTitle('Enter Serial Number')\ (3)
.WithInput(str, 'Serial Number')\ (4)
.WithOkButton().IsDefaultButton()\ (5) (6)
.WithCancelButton()\ (7)
.ThrowExceptionOnCancel()\ (8)
.Build()
result = dialog.Show() (9)
serial_number = result.Values[0] (10)| 1 | Add the .NET assembly Loehnert.Controls.dll to the CLR as a reference |
| 2 | Create a DialogueBuilder |
| 3 | Add a title |
| 4 | Add an input field for a character string |
| 5 | Add OK button |
| 6 | Set OK button as default button which reacts to the Enter key |
| 7 | Add cancel button |
| 8 | An exception should be thrown on cancellation (see OperationCanceledException), this leads to the script being cancelled |
| 9 | Display dialogue |
| 10 | Get the serial number from the result of the dialogue |
| Find further examples of dialogues in the DialogBuilder documentation. |
Display a dialog and wait for a code input
This example shows how to create a user dialog that prompts for code entry via keyboard or by scanning a code. When user input is received or when scanning is complete, the user dialog closes.
import clr
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.Controls')
from Loehnert.Controls.Dialogs import DialogService
dialog = None
code = None
def code_scanned_callback(object, args): (1)
global code (2)
code = args
if dialog is not None:
dialog.Close('CodeScanned')
Scanner.CodeScanned += code_scanned_callback (3)
try:
dialog = DialogService.GetDialogBuilder()\
.WithTitle('Enter a code')\
.WithMessage('Please scan the code or enter it using the keyboard.')\
.WithInput(str, 'Code').Left()\
.WithOkButton().IsDefaultButton()\
.WithCancelButton().ThrowExceptionOnCancel()\
.Build()
task = dialog.ShowAsync()
result = task.Result
finally:
Scanner.CodeScanned -= code_scanned_callback (4)
actual_code = code if code is not None else result.Values[0]
print str('actual_code: ' + actual_code)| 1 | Callback that is executed when a code is scanned |
| 2 | In order to be able to change the code variable that was created outside the function, this variable must be global |
| 3 | Attach to the CodeScanned event |
| 4 | Der Callback must be detached |
Threading
This shows how you can execute a function parallel to the main thread. The asynchronous function can be aborted.
import threading
def async_operation(stop): (1)
while True:
if stop():
break
stop_threads = False
t1 = threading.Thread(target = async_operation, args = (lambda : stop_threads, ))
t1.start()
try:
# Run here synchronous code
finally:
stop_threads = True
t1.join()| 1 | The stop parameter is a function that returns whether the asynchronous function should be aborted |
Logging
This example creates a logger and generates a log entry.
import clr
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.Lisrt')
from Loehnert.Lisrt.Messaging import MessageService
from Loehnert.Lisrt.Contracts import LogLevel
logger = MessageService.Instance.LoggerFactory.GetLogger('MyLogger') (1)
logger.Log(LogLevel.Info, 'This is a log entry with the log level Info') (2)| 1 | Create a logger with the name MyLogger |
| 2 | Create a log entry with the log level Info |
Type data inheritance
The following example shows how type data can be combined using Inheritance.
import clr
clr.AddReference('Caliburn.Micro')
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.TypeAndResult')
clr.AddReference('Loehnert.Lisrt.TypeAndResult')
from Caliburn.Micro import IoC
from Loehnert.TypeAndResult import TypeData as type_data_class
from Loehnert.TypeAndResult.Provider import ITypeDataProvider
from Loehnert.Lisrt.TypeAndResult.GeminiModule import GeminiTypeDataModule
def combine_type_data(types):
provider = IoC.Get[GeminiTypeDataModule]().DefaultProvider # type: ITypeDataProvider (1)
combined_type_data = None
for type_identifier in types:
current_type_data = provider.Load(type_identifier)
combined_type_data = current_type_data if combined_type_data == None else type_data_class.Inherit(combined_type_data, current_type_data) (2)
return combined_type_data
types = ['Type_A', 'Type_B', 'Type_C']
type_data = combine_type_data(types)
type_data.TypeIdentifier = 'MySuperType' (3)
TypeData.SetTypeData(type_data) (4)| 1 | Get standard type data provider (e.g. XML file data source) |
| 2 | Inherit type data |
| 3 | The combined type data is given a new name |
| 4 | Load the type data into the type data module |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! If you have any suggestions for improvement write to us.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us what we can improve.